Data Collections¶
Often times when building an integration scenario, you need to be able to store, query and retrieve arbitrary bits of data.
Some examples of things you might need to store:
- Mapping from users in Lucy to users in an HR system
- Storing details about devices including their IP addresses or other information required to communicate with them
- Storing the status of various requests and objects created by users.
Data Collections are perfect for this task.
A data collection is essentially a container for storing arbitrary documents. You can add documents to a collection, delete and update documents from a collection as well as query the collection to retreive documents that match a certain criteria.
Each document in a collection is just a JSON-based object. There is no fixed structure or schema for a collection. Each model can have multiple collections.
Note
Even though you could, in theory, store all your data in one large collection, it is generally recommended to have different collections for different kinds of data. Even though there is no structure imposed on each document in a collection, in practice, it’s recommended that all documents in a collection share the same structure.
There two entities involved in Data Collections,
Collection¶
A collection is the container in which you store your aribitrary data. Let’s look at some of the operations you can perform on a collection.
Creating a Collection¶
The following steps illustrate creating a data collection,
- Open model collections
- Choose Create a collection
- Give a name & press Enter or the tick icon
- To cancel, click on Delete button or press Escape
You should see the following result,
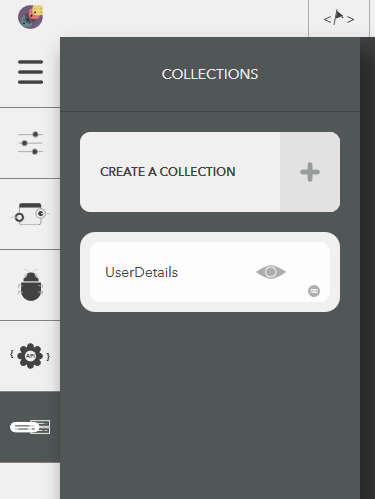
Illustration:

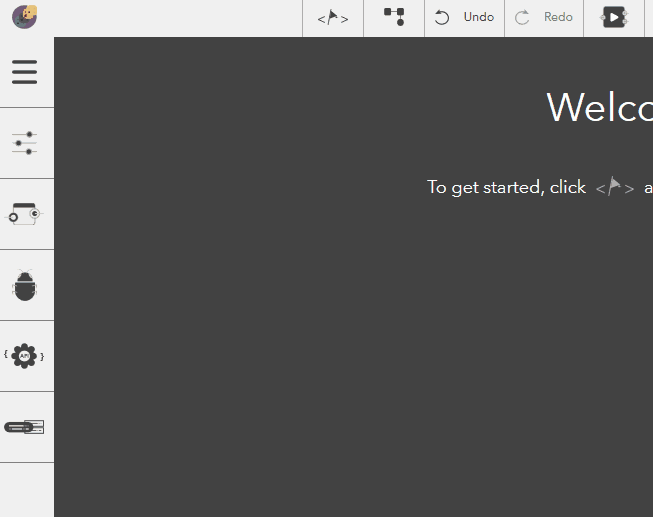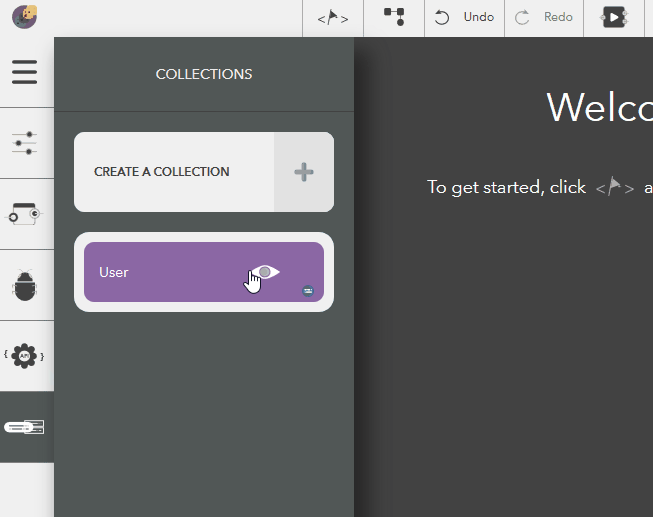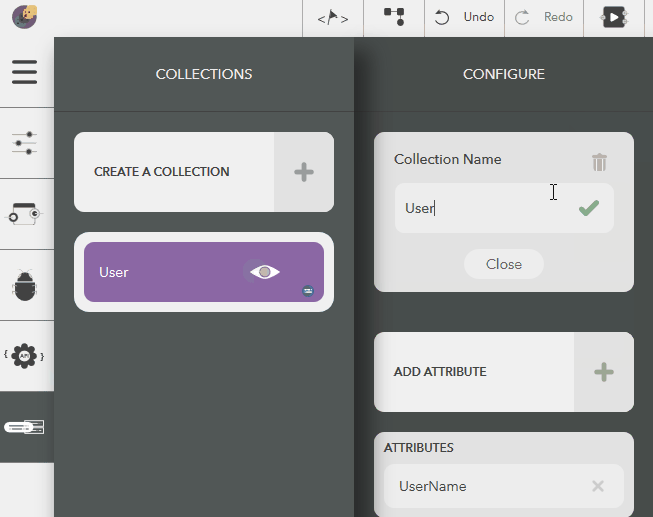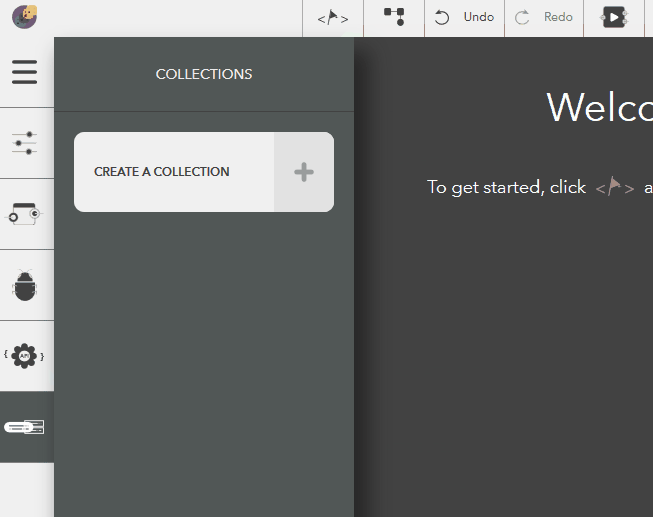
Updating a Collection¶
The following steps illustrate modifying a collection name,
- Choose the created collection by clicking on the eye icon,
- Click on Edit button next to the collection name in Configure pane
- Give a name & press Enter or the tick icon
- To cancel, click on Close button or press Escape
Illustration:
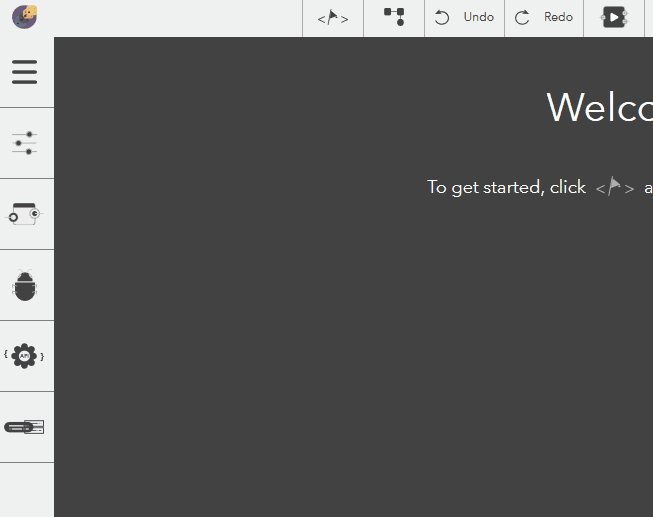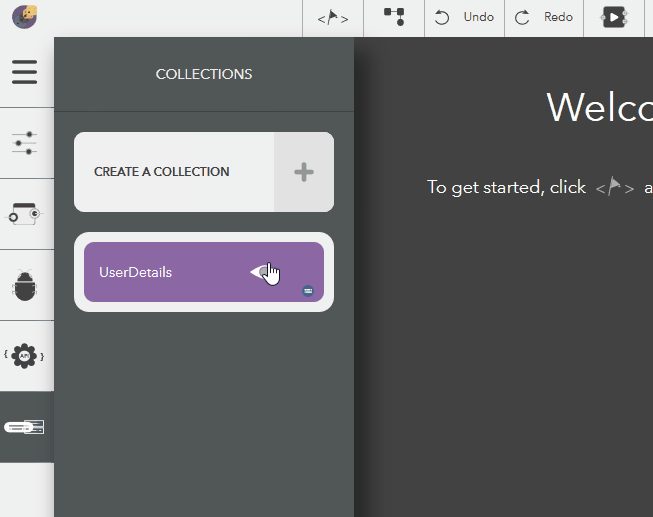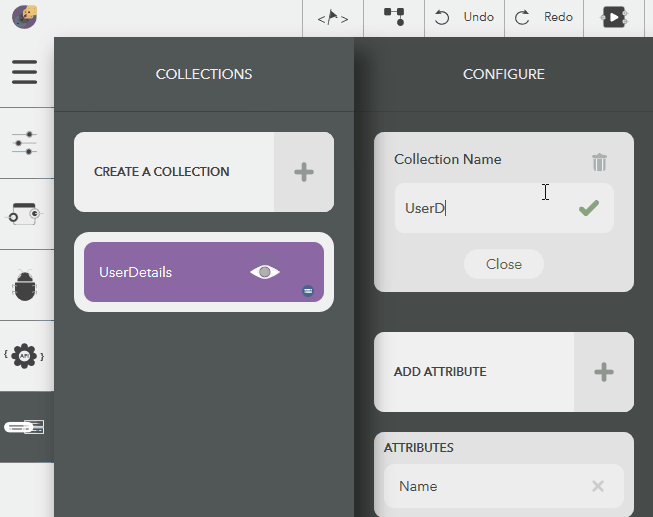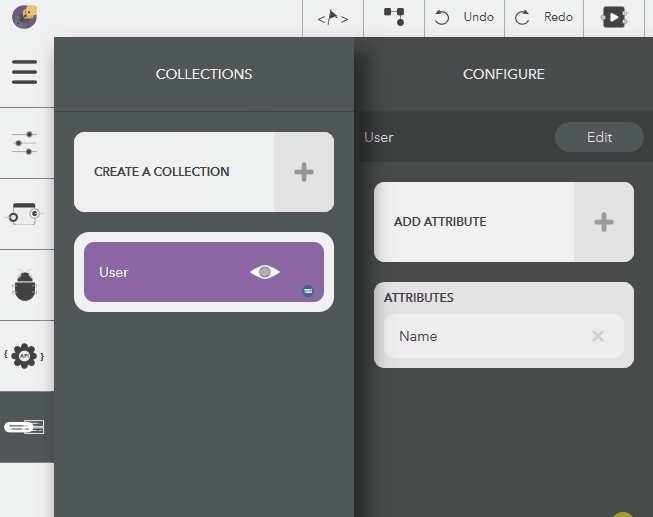
Deleting a Collection¶
The following steps illustrate deleting a collection,
- Choose the created collection by clicking on the eye icon,
- Click on Edit button next to the collection name in Configure pane
- Click on Delete button next to Collection Name
- To cancel, click on Close button or press Escape
Illustration:
Attributes¶
Attributes give the collection a structure & general sense about the data the collection stores. Let’s look at some of the operations you can perform on a collection.
Creating an Attribute¶
The following steps illustrate creating attributes,
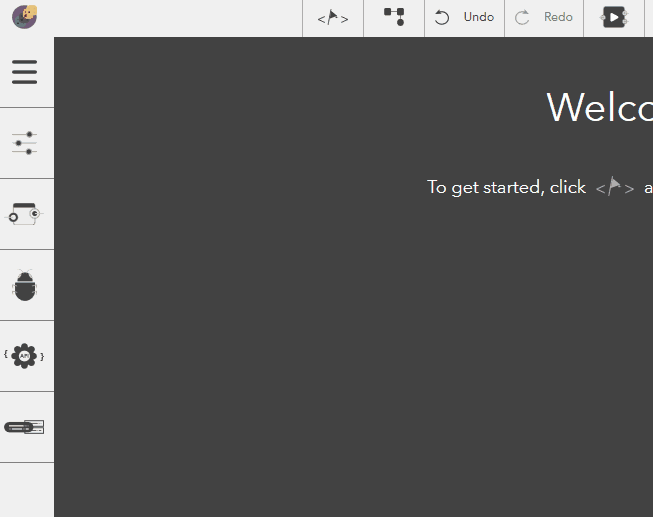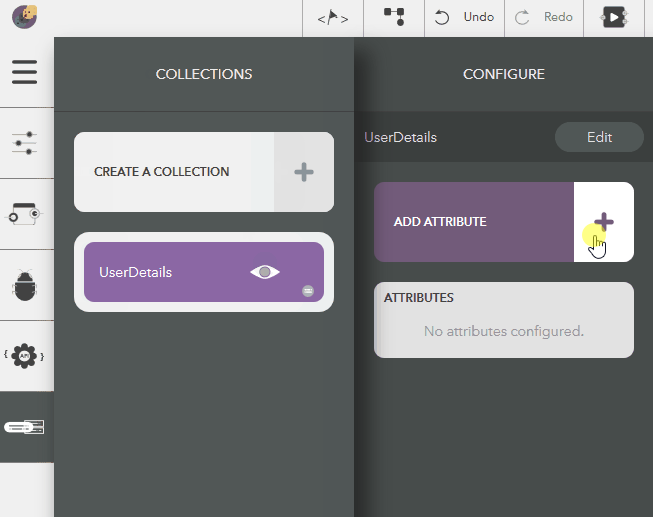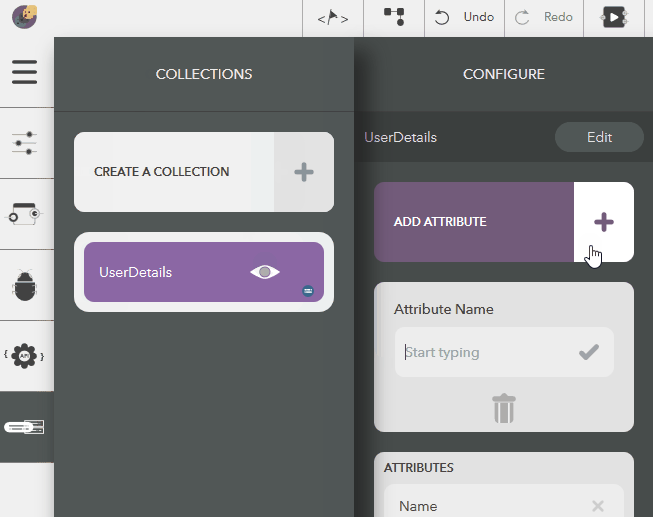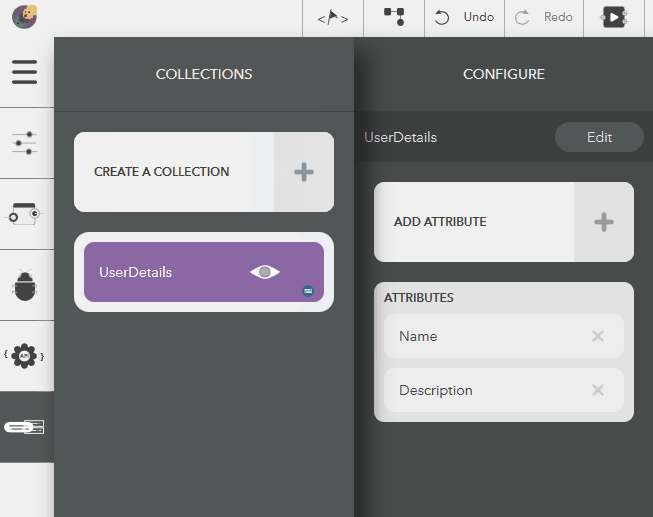
- Choose the created collection by clicking on the eye icon,
- Click on Add Attribute in the Configure pane
- Give a name & press Enter or the tick icon
- To cancel, click on Delete button or press Escape
You should see the following result,
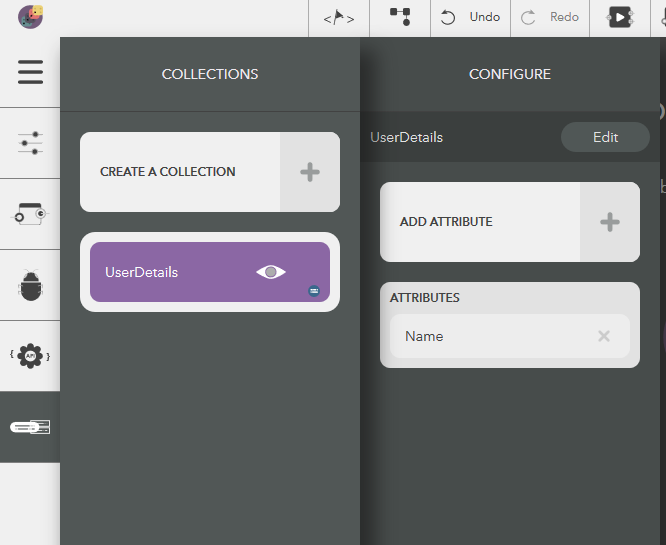
Illustration:
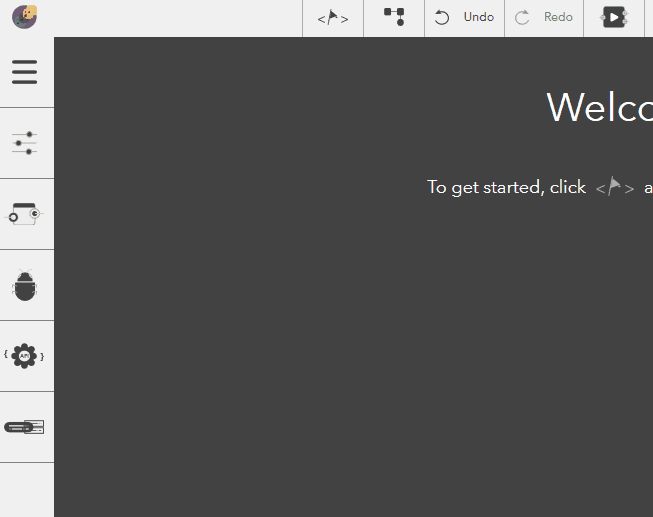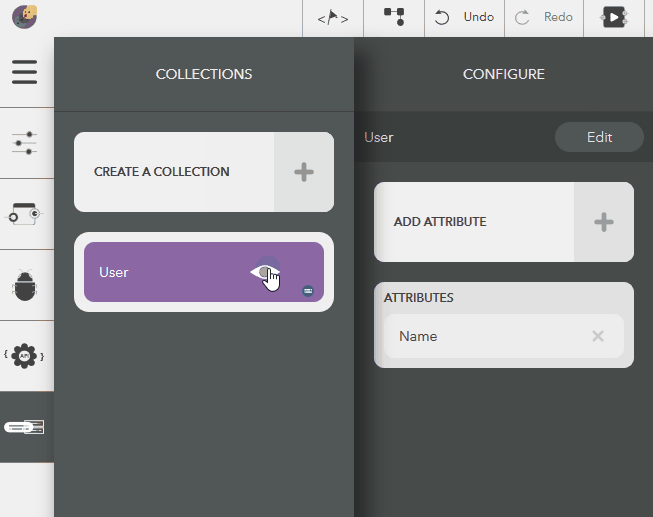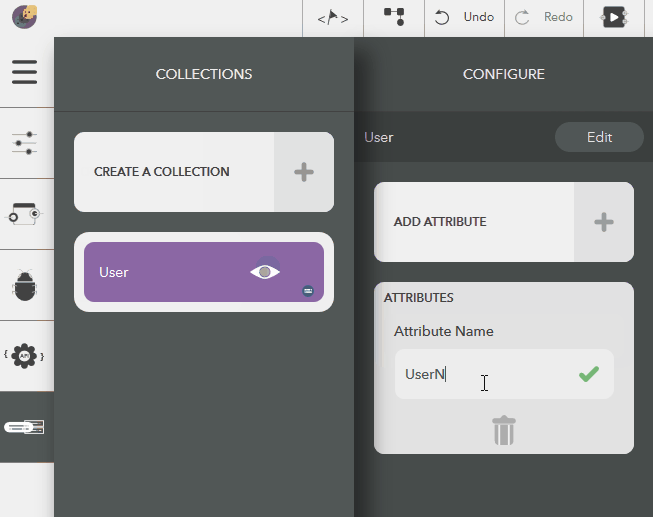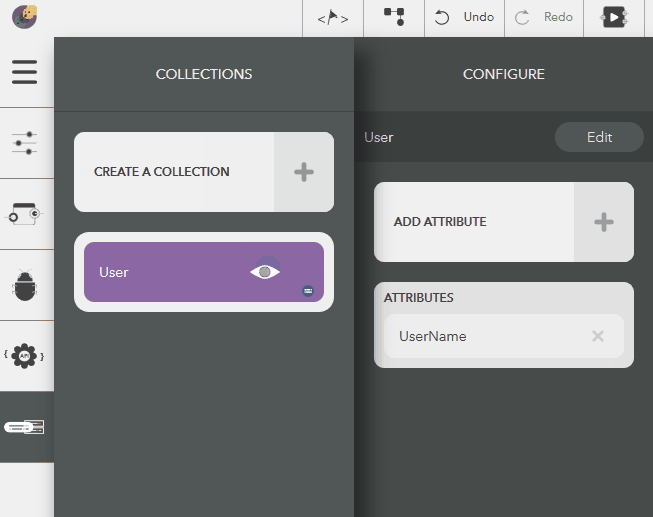
Updating an Attribute¶
The following steps illustrate modifying an attribute name,
- Choose the created collection by clicking on the eye icon,
- Click on an attribute from Attributes list in the configure pane
- Give a name & press Enter or the tick icon
- To cancel, click on Close button or press Escape
Illustration:
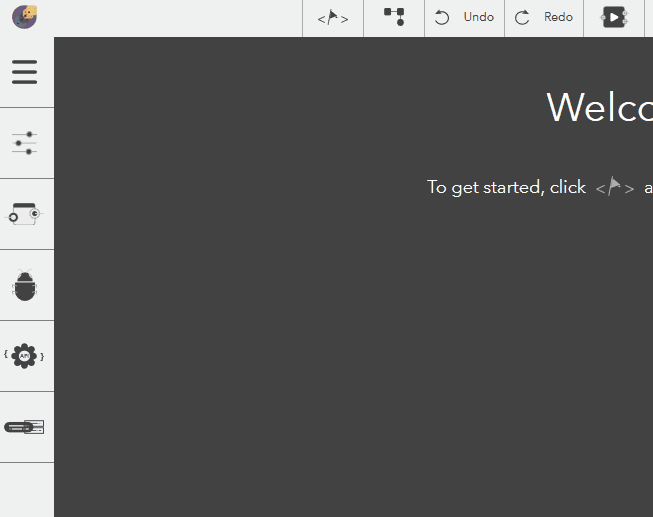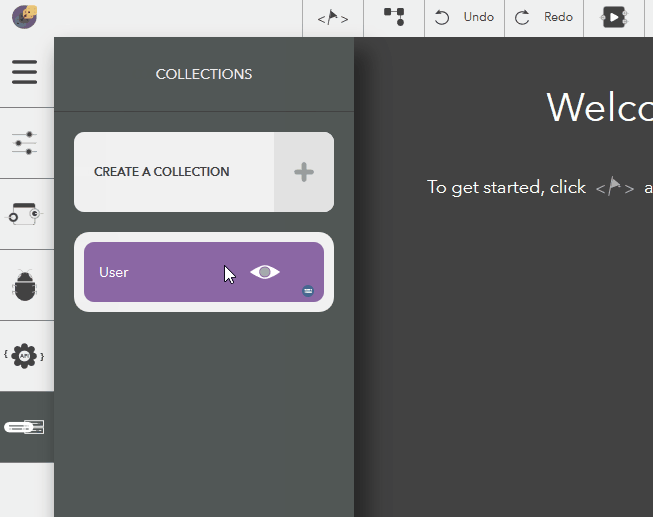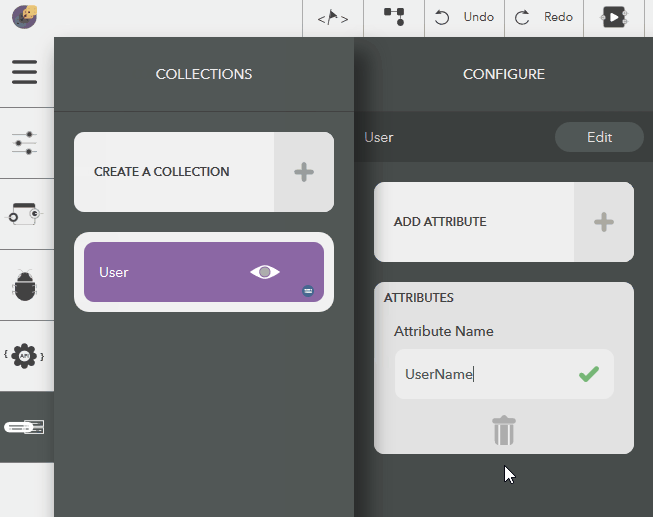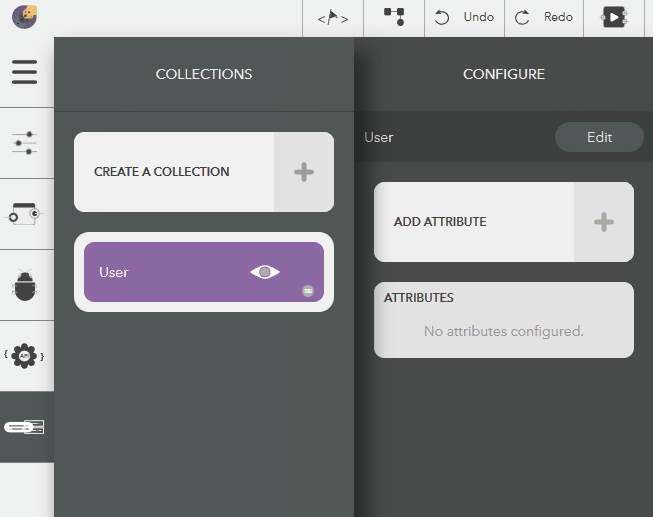
Deleting an Attribute¶
The following steps illustrate deleting a collection,
- Choose the created collection by clicking on the eye icon,
- Click on an attribute from Attributes list in the configure pane
- Click on Delete button to remove the attribute
- To cancel, click on Close button or press Escape
Illustration:
. note:
Your collection is document based and loosely structured. This means you can store any attributes and data you want in it - you are not restricted to the attributes you have defined.
The main reason for explicitly defining attributes is for documenting the intention of your data collection and to make it easy for Lucy to present configuration to you.
Working with Collections¶
So far, we saw how to define a collection & attributes. To actually write data into the collection & work on the data, you need to either use one of the blocks related to data collections or use our Javascript api.
Lucy Data Collection Blocks¶
Data collection blocks are Lucy blocks, that enable you to work with the collection you created earlier visually. The following blocks are provided for you and we will go through each of them in detail,
- Insert one document
- Insert all documents
- Find one document
- Find all documents
- Update one document
- Update all documents
- Replace one document
- Delete one document
- Delete all documents
- Count all documents
Insert one document¶
This block allows you to insert one document at a time. Document here can be explained with a simple analogy. If you have details about 10 users from User 1 to User 10, then each detail here can be consisdered a document. A document is a simple JSON structure, that looks like the following,
{
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
}
The following steps illustrate how you can insert a document,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Insert one document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- You can insert a document in couple of ways,
- Pass a JSON structure (default)
- Uncheck the Update data as attributes option from the block’s property menu.
- Use Make JSON Block, Javascript Block or ES6 Javascript Block to construct your JSON document
- Pass the output from the above block into Data pin of this block
- Pass individual attributes
- Check the Update data as attributes option from the block’s property menu.
- Set all input pins (not required) except Data pin in this block
Note
Regardless of how you insert a document, it gets stored in the JSON structure described above.
On the executing the action, you should see the following output for both methods described above,
{
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa0",
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
}
Illustration
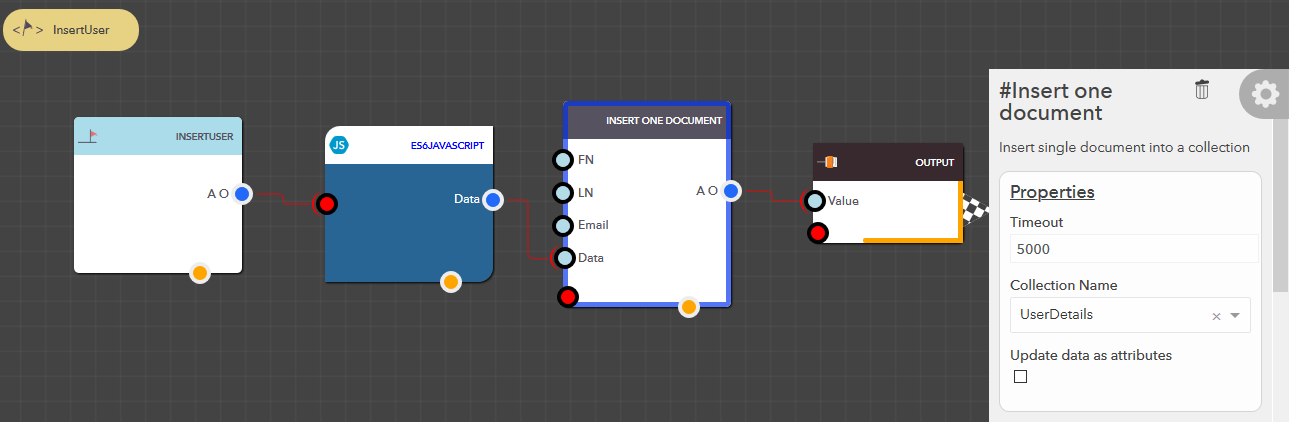
Insert all documents¶
This block allows you to insert multiple documents at a time. The following steps illustrate how you can insert all documents,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Insert all documents & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Use Make JSON Array Block, Javascript Block or ES6 Javascript Block to construct your JSON document
- Pass the output from the above block into Data pin of this block
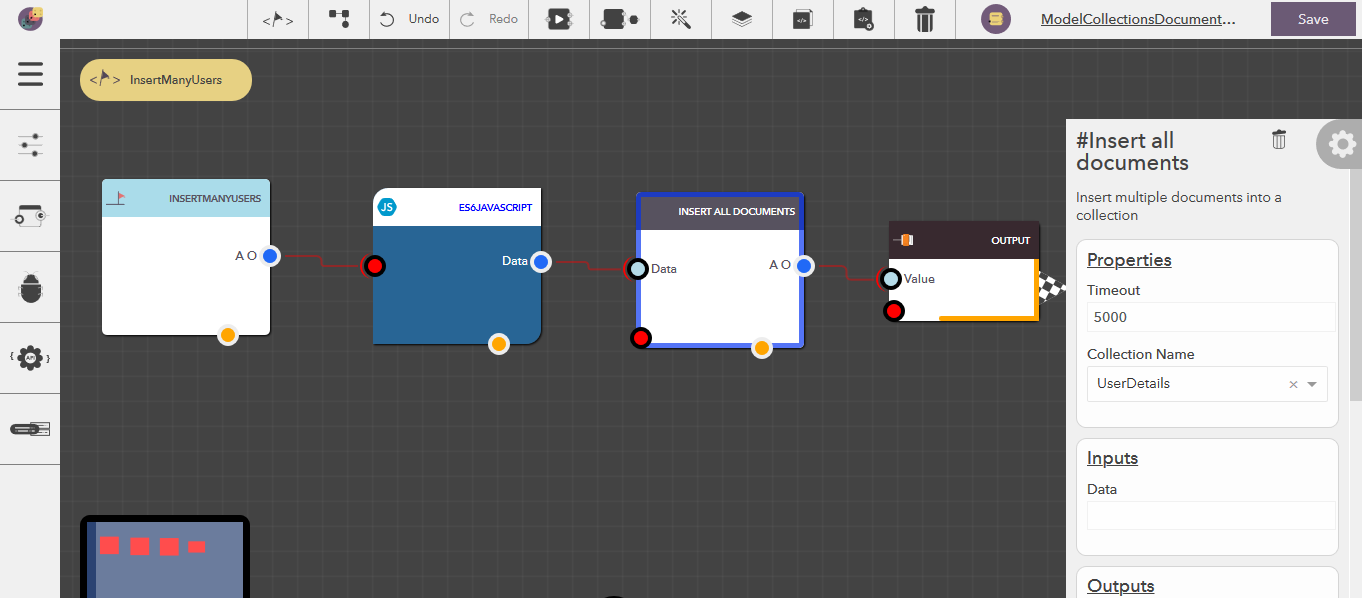
Filter Configuration¶
- Except for Insert one document and Insert all documents blocks, all the others have a common feature, which is the ability to perform an action on the collection based on filter conditions. Now, the filter conditions can be passed in a couple of ways,
- Using UI based filter
- Using Filter input pin
UI Filter¶
We will focus on UI filter configuration.
To access the filter configuration, click on Configure Collection in the block’s property editor or double on the block.
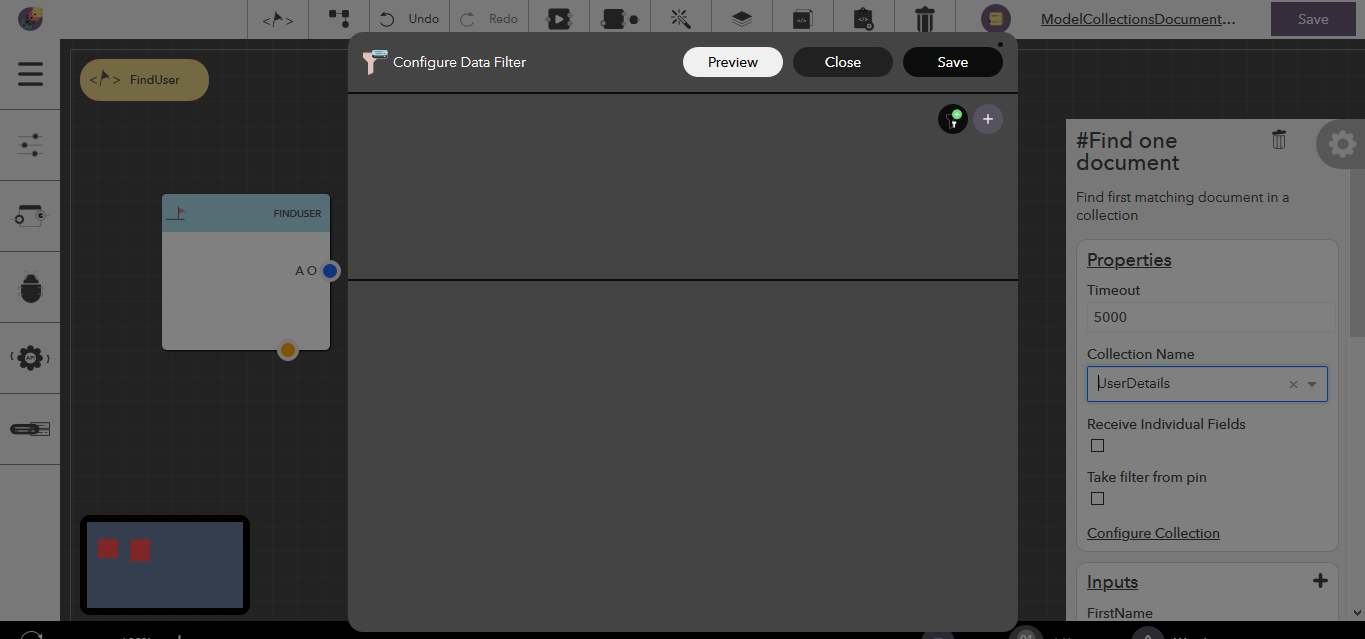
The following illustrates a sample filter configuration,
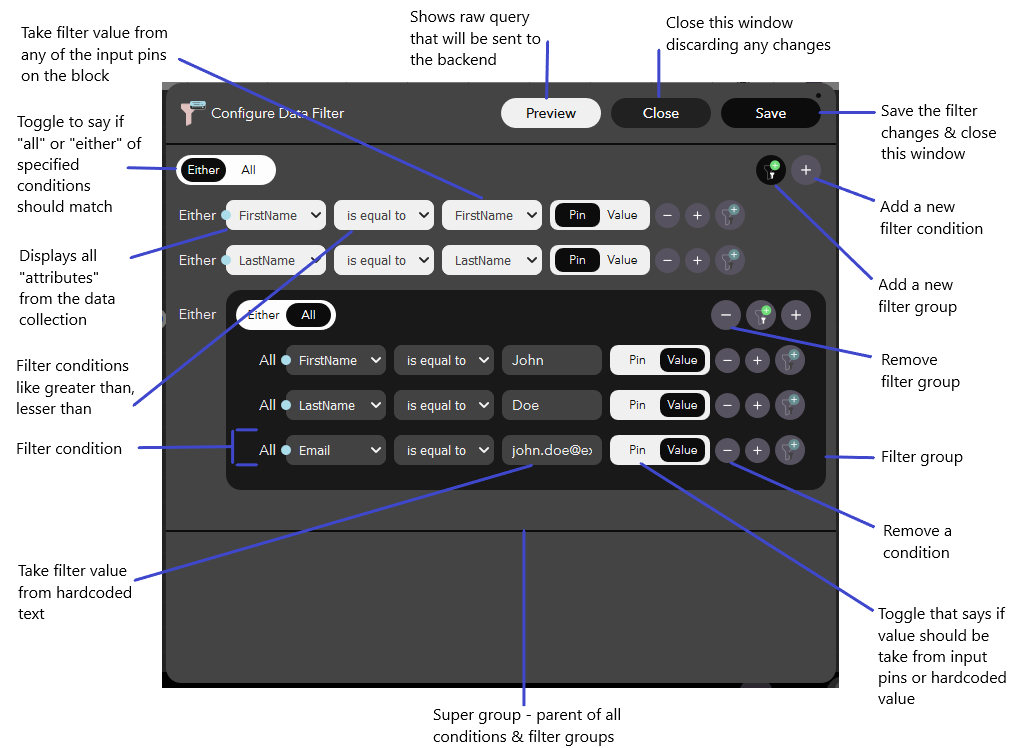
You could see from the sample that filter conditions aren’t flat, but nested within filter groups. This allows a rich & intuitive control over filtering your data. All filter conditions & filter groups are inside a default group called super group.
To add a filter condition,
- Click on

- Choose a value from the first dropdown box. These are your attributes from the collection
- Choose a filter condition from available options
- Use Pin/Value toggle switch, to either take the filter value from one of the block’s input pins (default) or from a harcoded value
To add a filter group,
- Click on

- Use Either/All toggle switch to decide if either or all the sub filter conditions & sub filter groups should pass for a successful match
The above process can go on repeatedly based on your filter requirements. Once you are done, you can see the raw query with Preview, save the changes with Save or discard the changes with Cancel.
Passing via Filter Input Pin¶
Right now data collections are powered by MongoDB in the backend. So, to pass a filter via input, you could use Make JSON Block, Javascript Block or ES6 Javascript Block to construct your JSON document. Checkout the available filter options here. Few sample filters are given below,
- Match all documents whose FirstName is John
{
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
}
- Match all documents whose FirstName is John and LastName is Doe
{
"$and": [
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}},
{"LastName": {"$eq": "Doe"}},
]
}
- Match all documents whose FirstName is John or LastName is Doe or if the Age is between 20 and 30
{
"$or": [
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}},
{"LastName": {"$eq": "Doe"}},
{
"$and": [
{"Age": {"$gt": 20}},
{"Age": {"$lt": 30}}
]
}
],
}
Find one document¶
This block allows you to find the first matching document from your data collection based on the filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can find a document,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Find one document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
- Outputs can be processed in the either of the follow ways,
- Extract collection’s attributes as separate output pins
- Check Receive Individual Fields property of the block
- Attributes available at their respective output pins
- Extract entire document (default)
- Uncheck Receive Individual Fields property of the block
- The entire document which would be available at available at All Output pin
Illustration
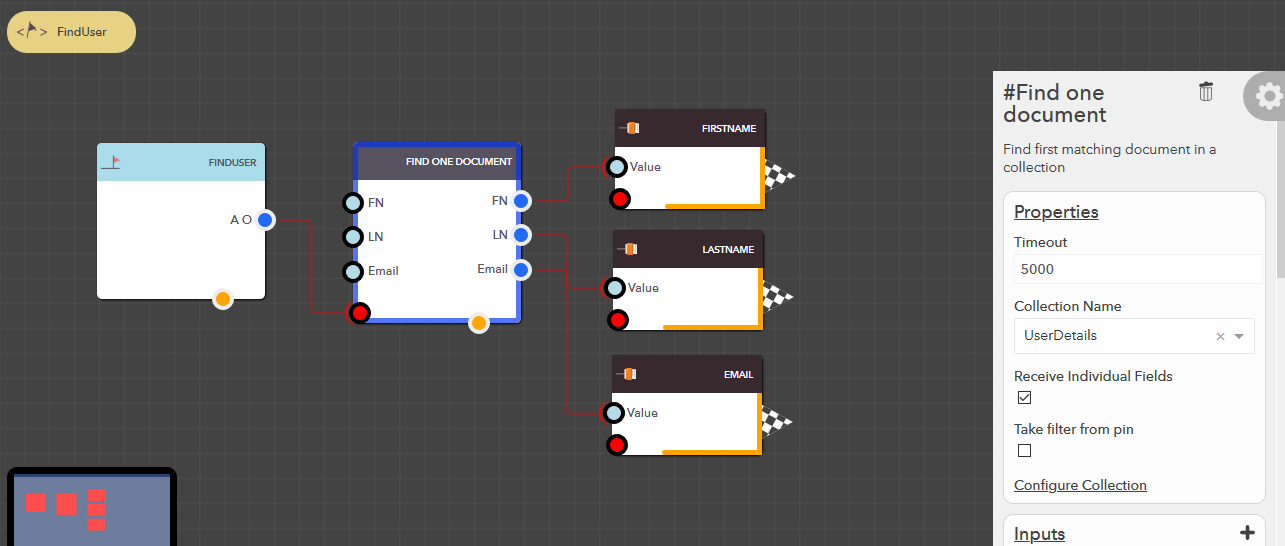
Find all documents¶
This block allows you to find all matching documents from your data collection based on the filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can find all documents,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Find all documents & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
Illustration
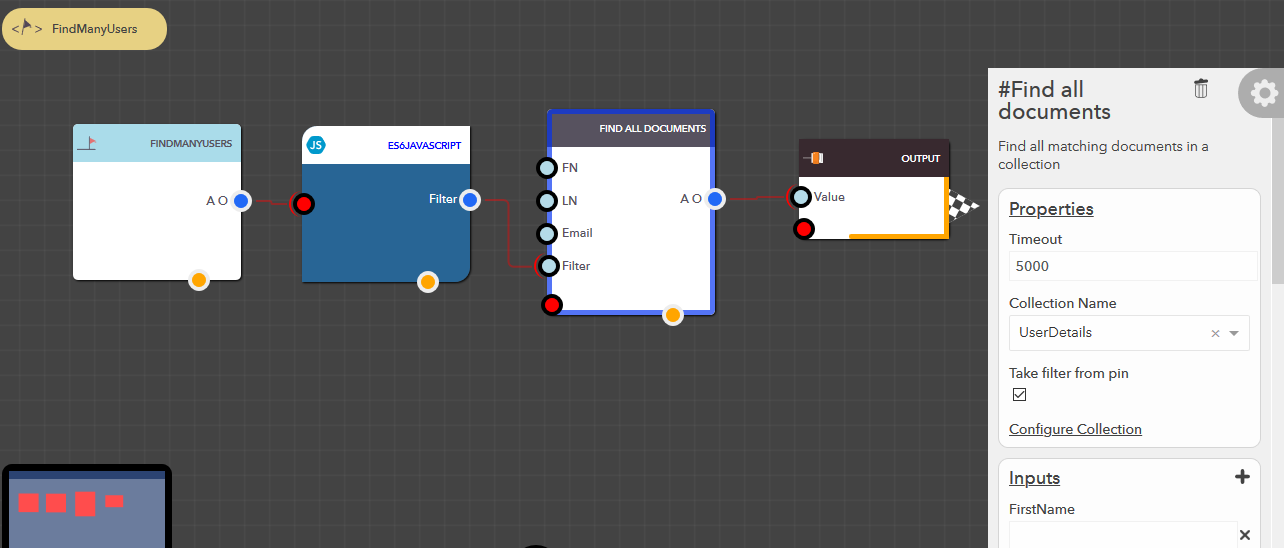
Update one document¶
This block allows you to update the first matching document in your data collection based on the data & filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can update a document,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Update one document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
- Data can be passed in couple of ways,
- Update individual attributes
- Check Update data as attributes property of the block
- Pass value the for the attributes at their respective input pins
- Pass entire document (default)
- Uncheck Update data as attributes property of the blocks
- Pass the document to Data input pin
Sample Output
{
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1
}
Note
Here, modifiedCount could be 0, if matching document was found, but data passed is same as the existing one.
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection. In which case you will see the following output,
{
"matchedCount": 0,
"modifiedCount": 0,
"_id": "5e25b5636725d689afccf6e7"
}
Illustration
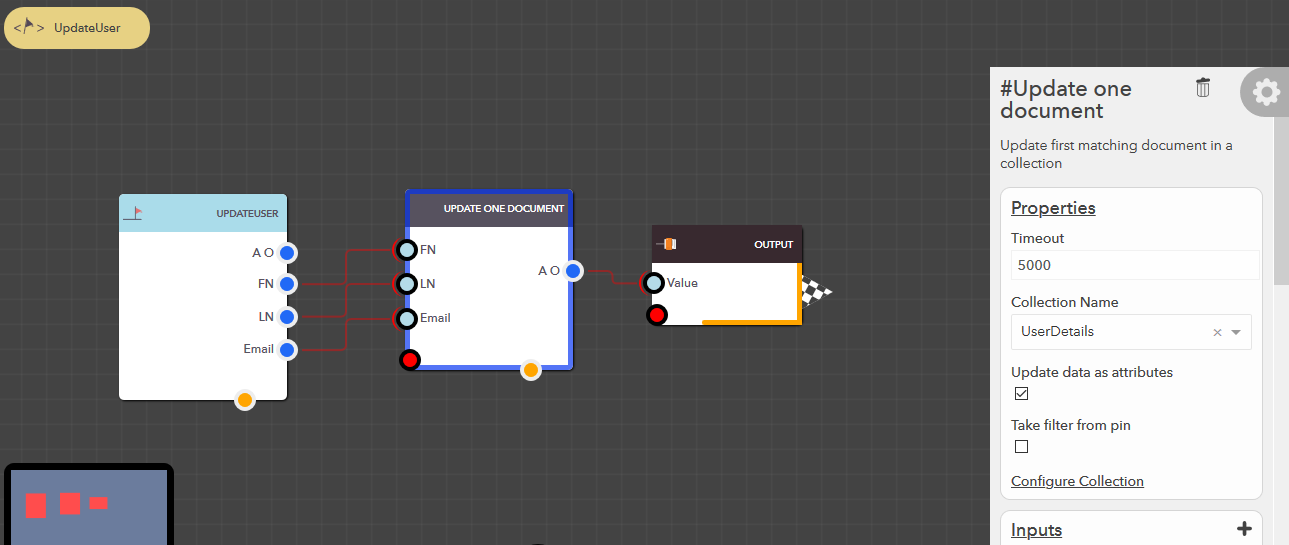
Update all documents¶
This block allows you to update all matching documents in your data collection based on the data & filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can update all documents,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Update all documents & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
- Data can be passed in couple of ways,
- Update individual attributes
- Check Update data as attributes property of the block
- Pass value the for the attributes at their respective input pins
- Pass entire document (default)
- Uncheck Update data as attributes property of the blocks
- Pass the document to Data input pin
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection.
Illustration
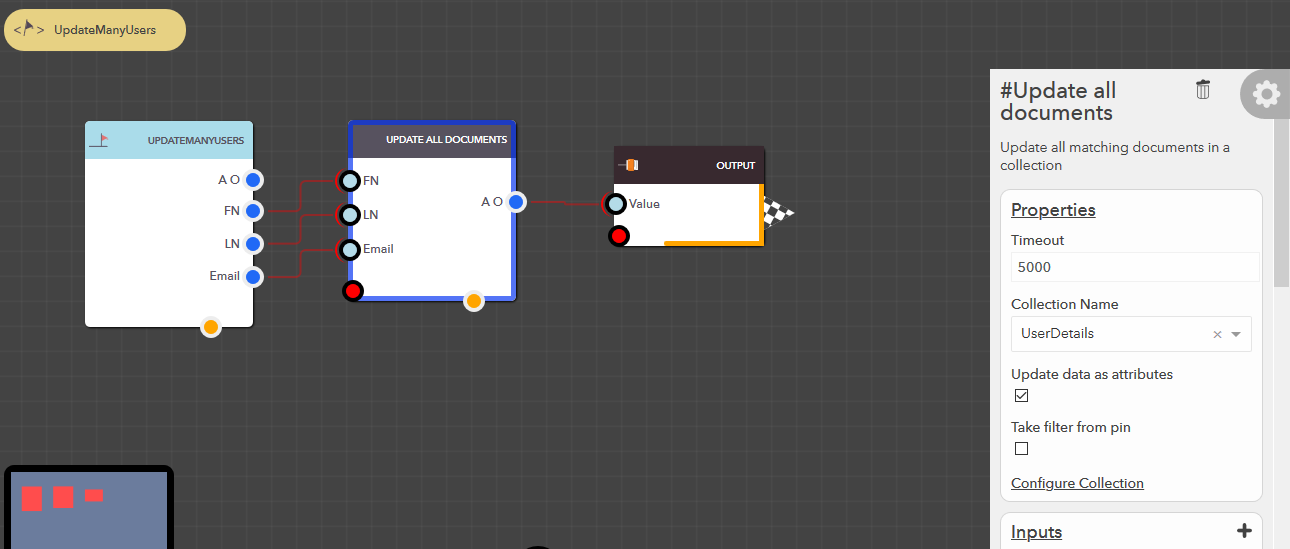
Replace one document¶
This block allows you to delete the first matching document entirely in your data collection based on the data & filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can replace a document,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Replace one document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
- Data can be passed in couple of ways,
- Update individual attributes
- Check Update data as attributes property of the block
- Pass value the for the attributes at their respective input pins
- Pass entire document (default)
- Uncheck Update data as attributes property of the blocks
- Pass the document to Data input pin
Tip
The main difference from Update one document is that, you can replace entire document with a new one. But, with Update one document you can update individual fields in the document.
For example, if you update the document {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”} with {“Age”: 28}, the final state of the document would be {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”, “Age”: 28}.
While, if you replace the document {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”} with {“Age”: 28}, the final state of the document would be {“Age”: 28}.
Sample Output
{
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1
}
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection. In which case you will see the following output,
{
"matchedCount": 0,
"modifiedCount": 0,
"_id": "5e25b5636725d689afccf6e7"
}
Illustration
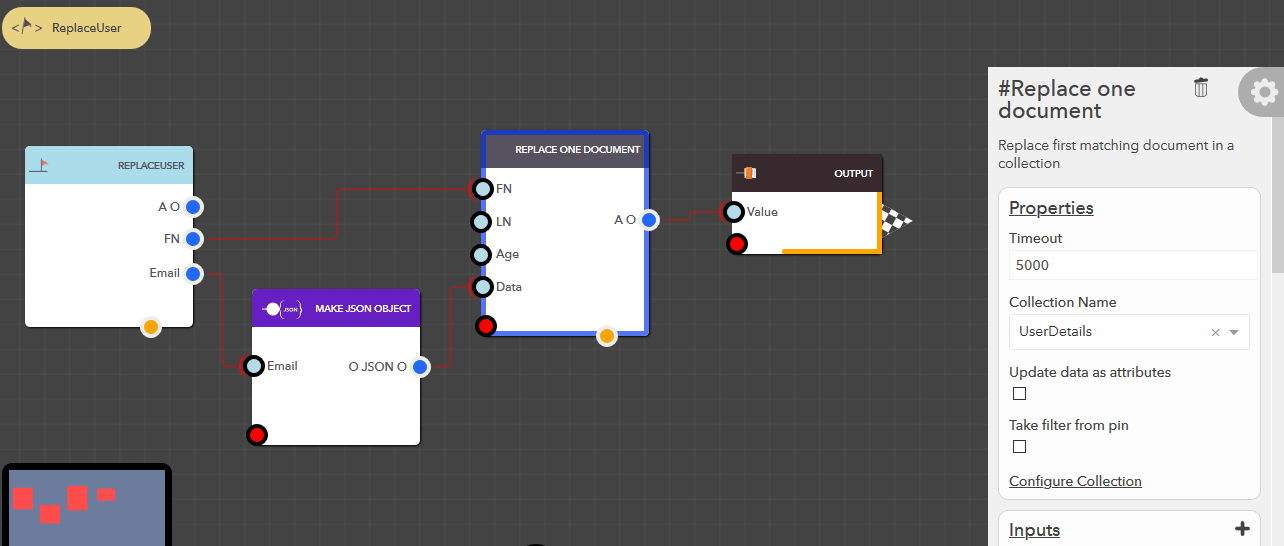
Delete one document¶
This block allows you to delete the first matching document in your data collection based on the filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can delete a document,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Delete one document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
Illustration
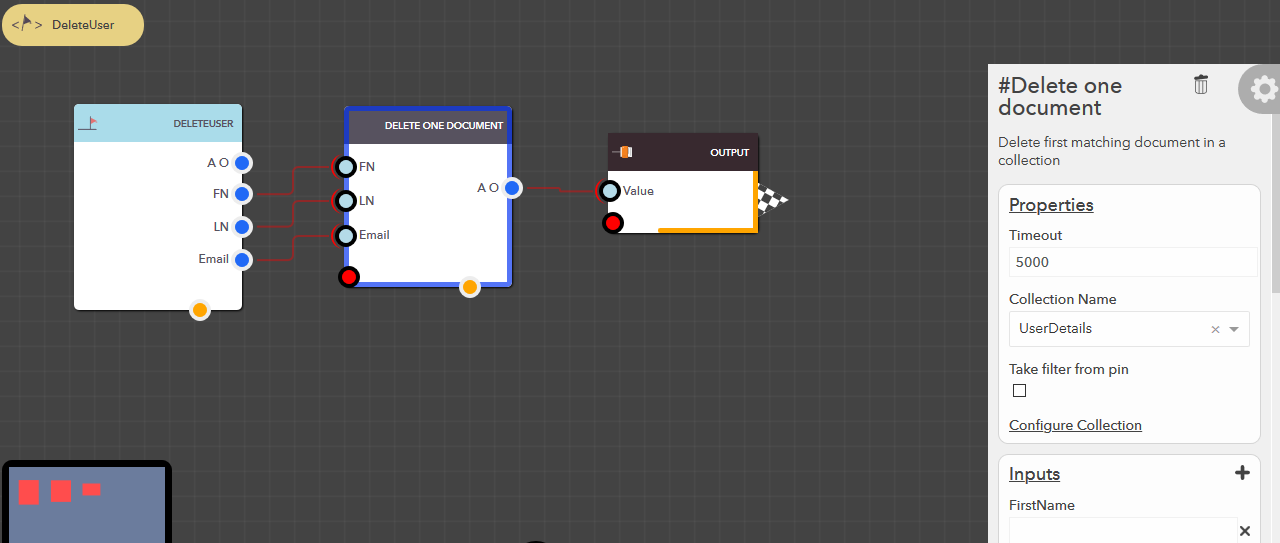
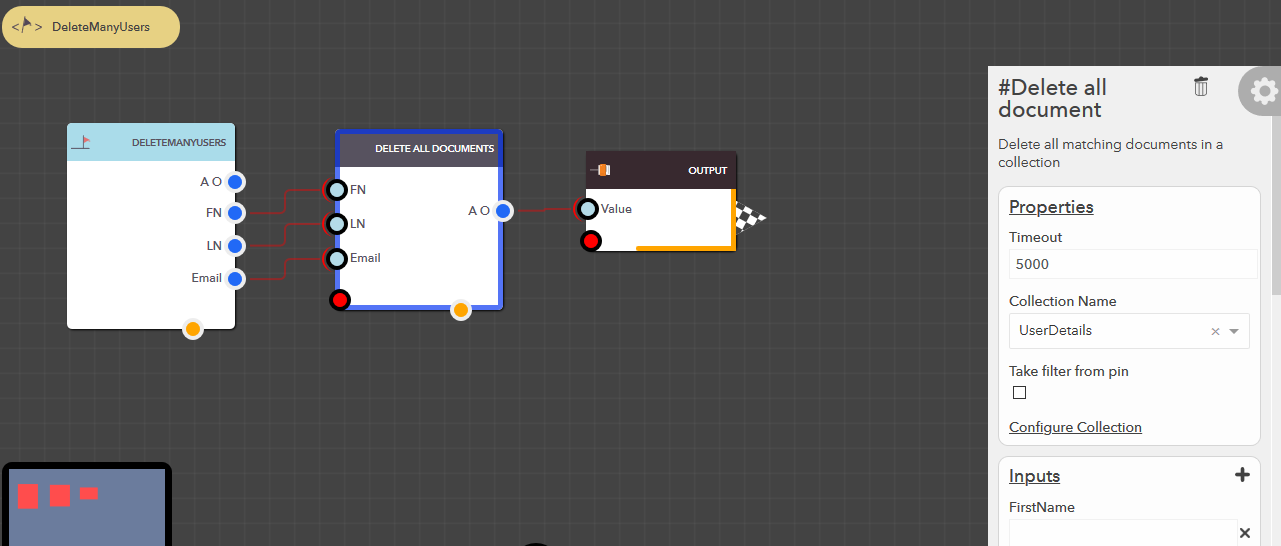
Delete all documents¶
This block allows you to delete all the matching documents in your data collection based on the filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can delete all documents,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Delete all document & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
Illustration
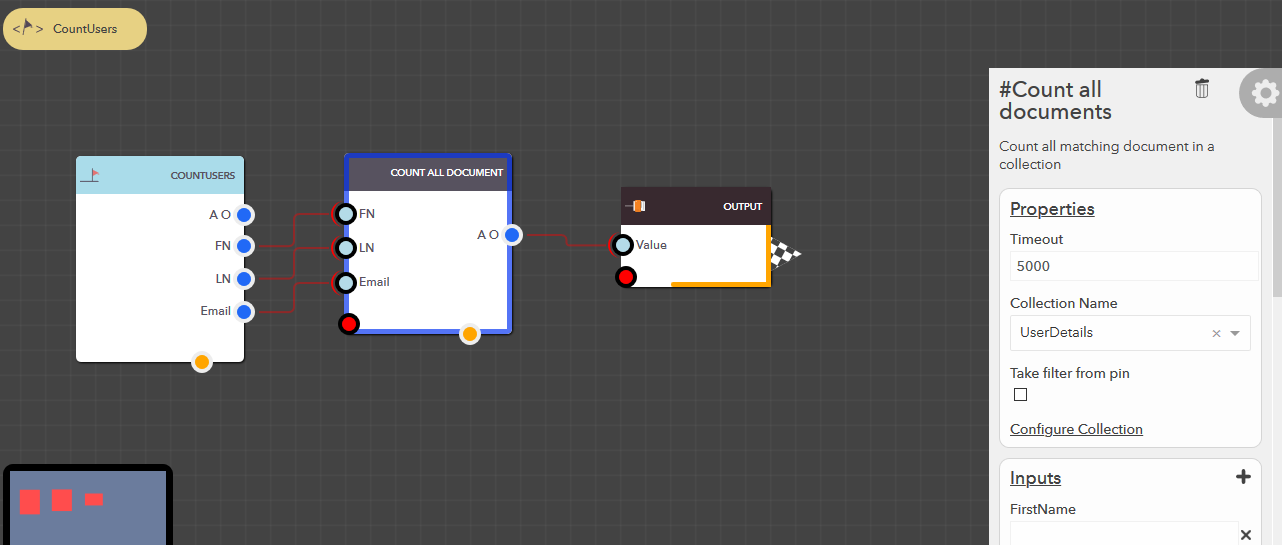
Count all documents¶
This block allows you to count all the matching documents in your data collection based on the filter conditions provided. The following steps illustrate how you can count all documents,
- From the blocks menu, choose Collections -> Count all documents & add it to you lucy action
- From the block’s property menu, choose a collection from Collection Name dropdown
- Filters can be passed in couple of ways,
- Pass filter as input
- Check Take filter from pin property of the block
- Pass the data to Filter input pin
- Take filter from configuration (default)
- Uncheck Take filter from pin property of the block
- Configure the filter as detailed in Filter Configuration section
Illustration
Javascript Data Collection API¶
When you need more control while passing data to your collection or when processing the outputs, you can make use of Data Collection API provided via ES6 Javascript Block. The following API’s are provided for you and we will go through each of them in detail,
- insertOne
- insertMany
- findOne
- findMany
- updateOne
- updateMany
- replaceOne
- deleteOne
- deleteMany
- count
- aggregate
Note
Since, data colletions are part of the Lucy model, they are exposed under the model in ES6 Javascript block. To access them, you could do as follows,
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("<model_name>");
let collections = model.collections();
Note
All the API’s below return a Javascript Promise, you can checkout more details about it & how to use them here.
insertOne¶
Insert one document at a time.
Syntax
collections.insertOne("<collection_name>", "<document>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to store the document under |
| document | JSON document | true | Document to be stored |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Document that was inserted into the collection {
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa0",
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
}
|
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let document = {
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
};
let options = {};
collections.insertOne("User", document, options)
.then(result => {
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
insertMany¶
Insert multiple documents at a time.
Syntax
collections.insertMany("<collection_name>", "<documents>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to store the documents under |
| documents | JSON document | true | Array of documents to be stored |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let documents = [
{
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
},
{
"FirstName": "Jane",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "jane.doe@example.com"
},
{
"FirstName": "Josh",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "josh.doe@example.com"
}
];
let options = {};
collections.insertMany("User", documents, options)
.then(result => {
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
findOne¶
Find the first matching document for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Syntax
collections.findOne("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to find the documents |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | First document that matched the filter condition {
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa0",
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
}
|
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let options = {};
collections.findOne("User", filter, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
findMany¶
Find all matching documents for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Syntax
collections.findMany("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to find the documents |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Array of documents that matched the filter condition [
{
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa0",
"FirstName": "John",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com"
},
{
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa1",
"FirstName": "Jane",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "jane.doe@example.com"
},
{
"_id": "5e21b3aecee5d8514cbfefa2",
"FirstName": "Josh",
"LastName": "Doe",
"Email": "josh.doe@example.com"
}
]
|
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let options = {};
collections.findOne("User", filter, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
updateOne¶
Update first matching document with the given data for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection. In which case you will get the following output,
{
"matchedCount": 0,
"modifiedCount": 0,
"_id": "5e25b5636725d689afccf6e7"
}
Syntax
collections.updateOne("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<data>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to update the documents for |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| data | JSON document | true | Document to be updated with |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Replacement result {
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1
}
Note Here, modifiedCount could be 0, if matching document was found, but data passed is same as the existing one. |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let data = {
{"LastName": "Carpenterr"}
};
let options = {};
collections.updateOne("User", filter, data, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
updateMany¶
Update all matching documents with the given data for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection. In which case you will get the following output,
{
"matchedCount": 0,
"modifiedCount": 0,
"_id": "5e25b5636725d689afccf6e7"
}
Syntax
collections.updateMany("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<data>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to update the documents under for |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| data | JSON document | true | Document to be updated with |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Replacement result {
matchedCount: 10,
modifiedCount: 10
}
|
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let data = {
{"LastName": "Carpenterr"}
};
let options = {};
collections.updateMany("User", filter, data, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
replaceOne¶
Replace first matching document is replaced with the given data for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Note
If no documents match the given filter, then a new document is created in the collection. In which case you will get the following output,
{
"matchedCount": 0,
"modifiedCount": 0,
"_id": "5e25b5636725d689afccf6e7"
}
Tip
The main difference from Update one document is that, you can replace entire document with a new one. But, with Update one document you can update individual fields in the document.
For example, if you update the document {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”} with {“Age”: 28}, the final state of the document would be {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”, “Age”: 28}.
While, if you replace the document {“FirstName”: “John”, “LastName”: “Doe”} with {“Age”: 28}, the final state of the document would be {“Age”: 28}.
Syntax
collections.replaceOne("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<data>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to replace the documents in |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| data | JSON document | true | Document to be replaced with |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Replacement result {
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1
}
Note Here, modifiedCount could be 0, if matching document was found, but data passed is same as the existing one. |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let data = {
{"FirstName": "Default"},
{"LastName": "User"},
{"Email": "default-user@example.com}
};
let options = {};
collections.replaceOne("User", filter, data, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
deleteOne¶
Delete first matching document for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Syntax
collections.deleteOne("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to delete the documents from |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let options = {};
collections.deleteOne("User", filter, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
deleteMany¶
Delete all matching documents for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Syntax
collections.deleteOne("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to delete the documents from |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let options = {};
collections.deleteMany("User", filter, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
count¶
Count all matching documents for the given collection & filter condition. More information on Filter Configuration.
Syntax
collections.count("<collection_name>", "<filter>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to count the documents from |
| filter | JSON document | true | Filter condition to filter documents by |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| number | Number of documents that matched the filter condition |
Example
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("UserModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let filter = {
{"FirstName": {"$eq": "John"}}
};
let options = {};
collections.count("User", filter, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
aggregate¶
Perform various aggration on your documents like sum, average, min, max, etc for the given collection.
Note
Right now data collections are powered by MongoDB in the backend. So, in order to use Aggregate Pipelines, checkout the documentation here
Syntax
collections.aggregate("<collection_name>", "<pipeline_stages>", "<options>");
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| collection_name | Text | true | Name of the collection to count the documents from |
| pipeline_stages | JSON document | true | Array of pipeline stages to process the data through for aggregation |
| options | JSON document | true (can be empty with no fields like {}) | Arbitrary Options to be passed to the data collection API |
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON document | Aggregation result |
Example
Here, we need to find the electricity usage of a city. So, we group the data by City in our data collection whose Usage is more than 50000, and calculate the sum from Usage field, and have the aggregation result in total field. The result would be,
[
{
"_id" : "New York",
"total": 123456789.0
},
{
"_id" : "London",
"total": 12345678.90
},
{
"_id" : "Mumbai",
"total": 1234567.890
},
{
"_id" : "Chennai",
"total": 123456.7890
}
]
let model = lucy.currentModel();
// or,
// let model = lucy.model("ElectricityMeterModel");
let collections = model.collections();
let pipelineStages = [
{ $match: { "Usage": { $gt: 50000 } } },
{ $group: { _id: "$City", total: { $sum: '$Usage' } }},
{ $sort: {total: -1} }
];
let options = {};
collections.aggregate("ElectricityMeterData", pipelineStages, options)
.then(result => {
// process result
runtime.done({});
})
.catch(error => {
runtime.error(error);
});
Arbitrary Options¶
This is provided in order to pass any additional configuration to the backend data collection API.
Tip
This may be modified with new features as the backend changes.
| Name | Data Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| limit | number | false | Maximum number of documents to return default is 0 |
| skip | number | false | Number of documents to skip that match the filter condition default is 0 |
| sort | number | false | Order to sort the matched documents 0 for ascending & 1 for descending default is 0 |